Can I leave my skin cancer alone?
Should I leave my skin cancer alone?
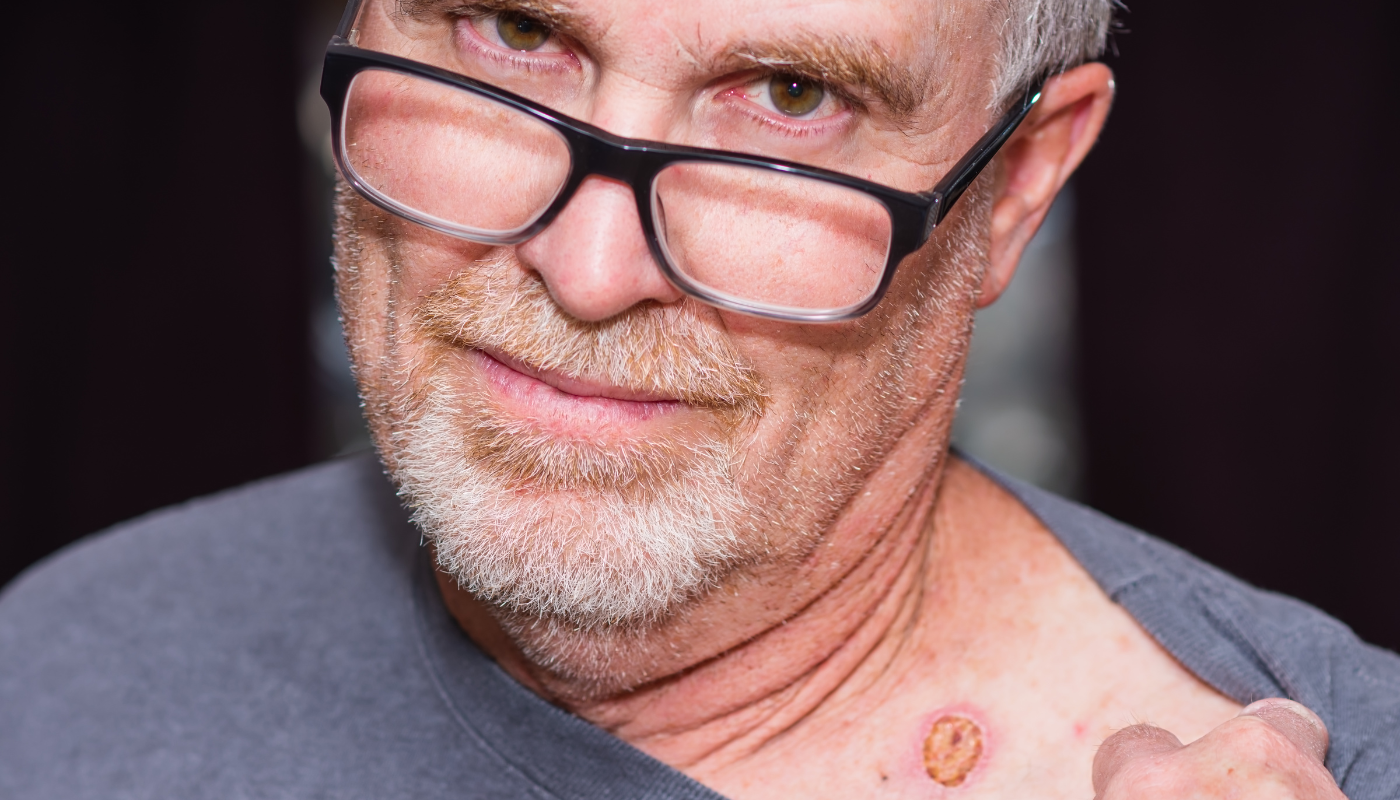
Skin cancer is the most prevalent form of cancer globally, with millions of new cases diagnosed each year.
Despite its high incidence, there remains a concerning question among some individuals: "Can I leave my skin cancer alone?"
Addressing this question requires a comprehensive understanding of the types of skin cancer, their potential progression if untreated, and the critical importance of early detection and treatment.
Types of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer primarily falls into three categories:
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): This is the most common type, originating in the basal cells of the epidermis. BCCs often appear as pearly or waxy bumps and are typically caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): Arising from the squamous cells, SCCs may present as firm, red nodules or flat lesions with a scaly surface. Like BCCs, they are commonly linked to UV exposure.
Melanoma: The most aggressive form, melanoma develops in the melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigment production. Melanomas can manifest as new moles or changes in existing moles and are notorious for their rapid ability to spread to other parts of the body.
The Risks of Leaving Skin Cancer Untreated
Choosing not to treat skin cancer can lead to severe consequences, varying by the type of cancer:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): While BCCs are generally slow-growing and have a low risk of metastasis, neglecting treatment can result in significant local tissue damage. They can invade surrounding tissues, including nerves and bones, leading to disfigurement and functional impairments. In rare cases, BCCs can metastasize, posing life-threatening risks.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): SCCs are more aggressive than BCCs and have a higher propensity to spread to lymph nodes and distant organs if left untreated. This progression can result in severe health complications and may become life-threatening.
- Melanoma: Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer due to its high likelihood of spreading (metastasizing) to other parts of the body. If not treated promptly, melanoma can advance rapidly, making treatment more challenging and significantly reducing survival rates.
The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection and intervention are paramount in managing skin cancer effectively:
- Survival Rates: When detected early, the five-year survival rate for melanoma is over 99%. However, this rate drops to 66% if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes and 27% if it has metastasized to distant organs. The Skin Cancer Foundation
- Treatment Outcomes: Early-stage skin cancers often require less invasive treatments and have higher cure rates. Delayed treatment can necessitate more extensive procedures, increasing the risk of complications and reducing the likelihood of a favorable outcome.

Treatment Modalities for Skin Cancer
Several effective treatments are available for skin cancer, tailored to the type, location, and stage of the disease:
Surgical Options:
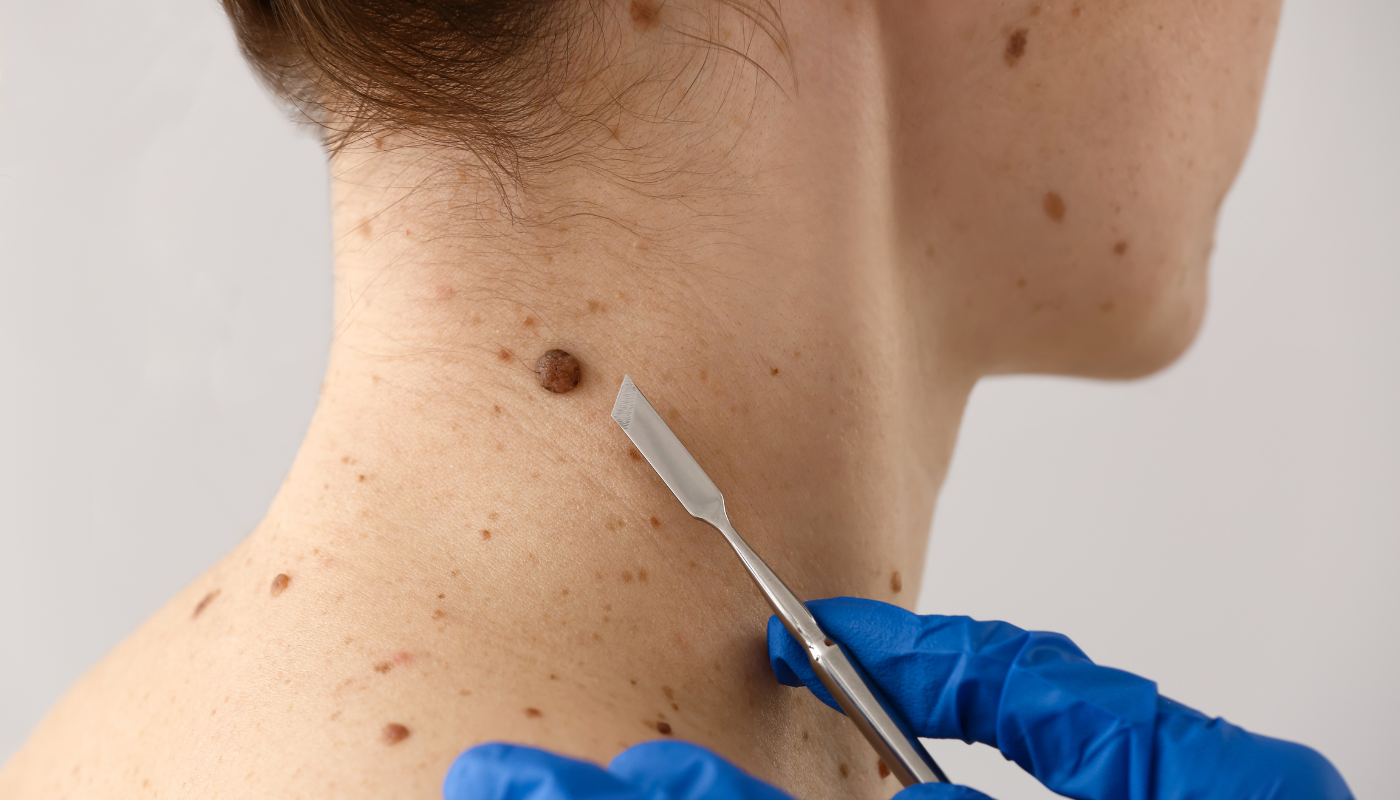
- Excisional Surgery: The tumor, along with a margin of healthy tissue, is surgically removed. This method is commonly used for various skin cancers.
- Mohs Surgery: This precise technique involves the step-by-step removal and microscopic examination of cancerous tissue until no abnormal cells remain. Mohs surgery is particularly effective for cancers in cosmetically sensitive areas, offering high cure rates while preserving healthy tissue.
Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Topical Medications: Creams or gels containing anti-cancer agents can be applied directly to certain superficial skin cancers.
- Cryotherapy: This treatment involves freezing cancer cells with liquid nitrogen, causing them to die and slough off.
- Radiation Therapy: Targeted radiation can destroy cancer cells, often used when surgery isn't an option.
- Photodynamic Therapy (PDT): Combining light-sensitive drugs with light exposure to destroy cancer cells.
Advanced Therapies for Metastatic Disease:
- Immunotherapy: Drugs such as nivolumab (Opdivo) and ipilimumab (Yervoy) enhance the immune system's ability to target and destroy cancer cells. These therapies have shown promising results, especially in advanced melanoma cases.
Case Studies Highlighting the Dangers of Inaction
Real-life cases underscore the critical importance of timely intervention:
- Delayed Treatment Leading to Advanced Disease: A patient who postponed seeking medical advice for a suspicious skin lesion experienced progression to advanced melanoma, requiring extensive treatment and facing a reduced prognosis.
- Misinterpretation of Symptoms: An individual mistook a persistent pimple for a benign issue, only to discover it was basal cell carcinoma. This highlights the necessity of consulting healthcare professionals for any unusual skin changes.
Conclusion
Choosing to leave skin cancer untreated is a perilous decision that can lead to severe health consequences, including disfigurement, metastasis, and even death.
Early detection and treatment are crucial, offering the best chances for successful outcomes and minimizing the extent of medical interventions required.
Regular skin examinations, both self-assessments and professional evaluations, play a vital role in identifying skin cancer at its earliest and most treatable stages. If you notice any new, changing, or suspicious skin lesions, it is imperative to consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Proactive management of skin health not only preserves physical well-being but also provides peace of mind, knowing that potential issues are addressed before they escalate.
More Skin Tips.
CoreBodi








| Powered by Kaptol Media


