Who is at Risk for Skin Cancer?
SKIN CANCER - WHO IS AT RISK?

Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide, affecting millions of people each year.
While anyone can develop skin cancer, certain factors increase the risk significantly.
Understanding who is most vulnerable can help individuals take proactive steps to protect themselves and detect skin cancer early when it is most treatable.
The Universal Risk: Why Everyone is Susceptible
Skin cancer does not discriminate—it can affect people of all ages, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
The primary cause of most skin cancers is ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and tanning beds, which can damage skin cells and lead to the development of cancerous growths.
While some individuals have a higher predisposition due to genetics or lifestyle factors, it is crucial to recognize that everyone is at some level of risk.
Therefore, sun protection and regular skin checks should be a priority for all.
Fair Skin and Skin Type: A Major Risk Factor
People with fair skin, especially those who burn easily and rarely tan, are at a higher risk of developing skin cancer.
This is because lighter skin contains less melanin, the pigment that provides some protection against harmful UV rays. Individuals with red or blonde hair, light-colored eyes, and freckles are particularly vulnerable to sun damage and, consequently, skin cancer.
However, it is essential to note that darker-skinned individuals are not immune and can also develop skin cancer, sometimes in areas less exposed to the sun, such as the palms, soles, and under the nails.
History of Sunburns and Cumulative UV Exposure
Experiencing multiple sunburns, especially in childhood and adolescence, significantly raises the risk of developing skin cancer later in life.
Sunburns indicate severe skin damage, and repeated exposure to intense sunlight can lead to genetic mutations in skin cells. Those who spend a lot of time outdoors without adequate sun protection—such as construction workers, farmers, and outdoor enthusiasts—are also at heightened risk due to cumulative UV exposure over the years.
The Role of Tanning Beds in Skin Cancer Risk
Artificial tanning is a major contributor to skin cancer risk.
Tanning beds emit concentrated UV radiation, which penetrates the skin deeply, causing DNA damage. Studies have shown that using tanning beds before the age of 35 increases the risk of melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, by up to 75%.
Despite the risks, many people still engage in indoor tanning, often under the misconception that it is safer than sun exposure.
Family History and Genetic Predisposition
Genetics play a significant role in skin cancer risk.
If a close relative—such as a parent or sibling—has been diagnosed with skin cancer, the likelihood of developing it increases. Certain genetic conditions, such as xeroderma pigmentosum, make individuals extremely sensitive to UV radiation and highly susceptible to skin cancer.
While genetics cannot be changed, those with a family history of skin cancer should be extra vigilant about sun protection and regular skin screenings.

Weakened Immune System and Skin Cancer Risk
The immune system helps the body fight off cancerous cells before they can develop into full-blown skin cancer.
However, individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk. This includes people with conditions such as HIV/AIDS, those undergoing chemotherapy, and organ transplant recipients who take immunosuppressive medications.
In these cases, the body is less capable of repairing damaged skin cells, making skin cancer more likely and potentially more aggressive.
Age and Skin Cancer: Why Risk Increases Over Time
Although skin cancer can occur at any age, the risk increases with time.
Older individuals have had more cumulative sun exposure over the years, which raises the likelihood of developing skin cancer. However, in recent years, melanoma rates have been rising among young adults, likely due to increased sun exposure and the popularity of tanning beds.
This shift highlights the need for awareness and early prevention across all age groups.
Geographical Location and UV Exposure
Where a person lives can significantly impact their risk of skin cancer.
Those residing in regions with intense sunlight, such as Australia, the southern United States, and high-altitude areas, face higher UV exposure levels.
Additionally, people who live near the equator receive stronger sun radiation year-round, increasing their chances of developing skin cancer.
Gender Differences in Skin Cancer Risk
Studies have shown that men and women have different skin cancer risks.
While young women are more likely to develop melanoma due to higher use of tanning beds, men over 50 are at a greater risk of skin cancer overall, particularly on areas like the scalp, ears, and back.
Men are also less likely to use sunscreen and undergo routine skin checks, which can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment.

Occupational and Lifestyle Risk Factors
Certain jobs and lifestyles expose people to higher levels of UV radiation.
Outdoor workers, such as farmers, lifeguards, landscapers, and construction workers, spend prolonged periods under direct sunlight, increasing their risk. Athletes who train outside without adequate sun protection also fall into this category.
Additionally, frequent travelers to sunny destinations should take extra precautions to protect their skin.
The Importance of Sun Protection and Regular Screenings
While some risk factors, such as genetics and age, cannot be controlled, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of skin cancer.
Protective measures include:
- Wearing broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily
- Seeking shade during peak sun hours (10 AM – 4 PM)
- Wearing protective clothing, wide-brimmed hats, and UV-blocking sunglasses
- Avoiding tanning beds and artificial tanning methods
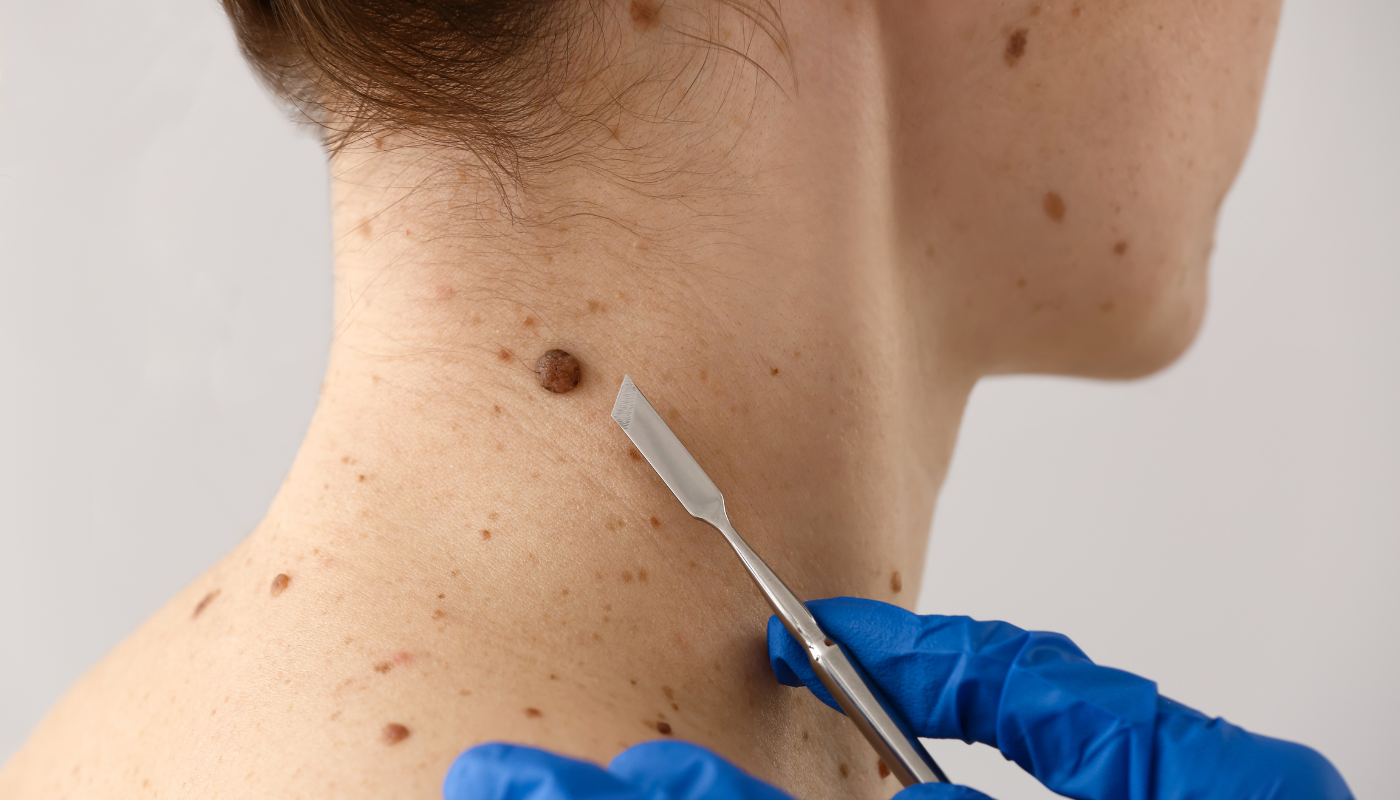
- Performing regular self-examinations to check for new or changing moles
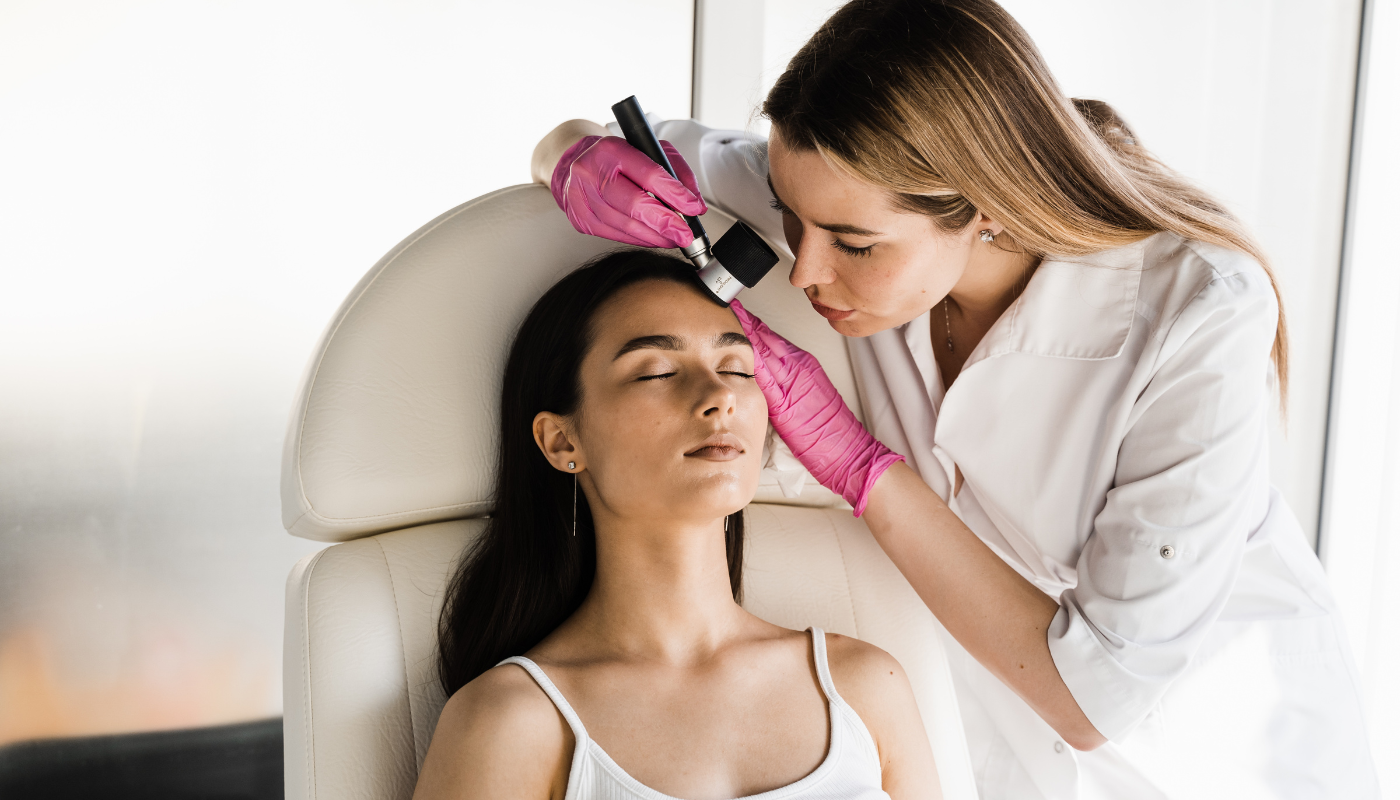
- Scheduling annual skin exams with a dermatologist, especially for those at high risk
Conclusion: Awareness and Prevention Are Key
Skin cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition, but it is also one of the most preventable forms of cancer.
Understanding the risk factors—ranging from fair skin and sun exposure to genetic predisposition and weakened immune systems—empowers individuals to take proactive steps in protecting themselves.
By adopting sun-safe behaviours and staying vigilant with skin checks, everyone can reduce their risk and improve early detection rates, leading to better outcomes and healthier skin for life.
More Skin Tips.
CoreBodi







| Powered by Kaptol Media


