Nodular Melanoma: What Does It Look Like
Nodular Melanoma: What It Looks Like, How to Recognize It, and What Causes It?
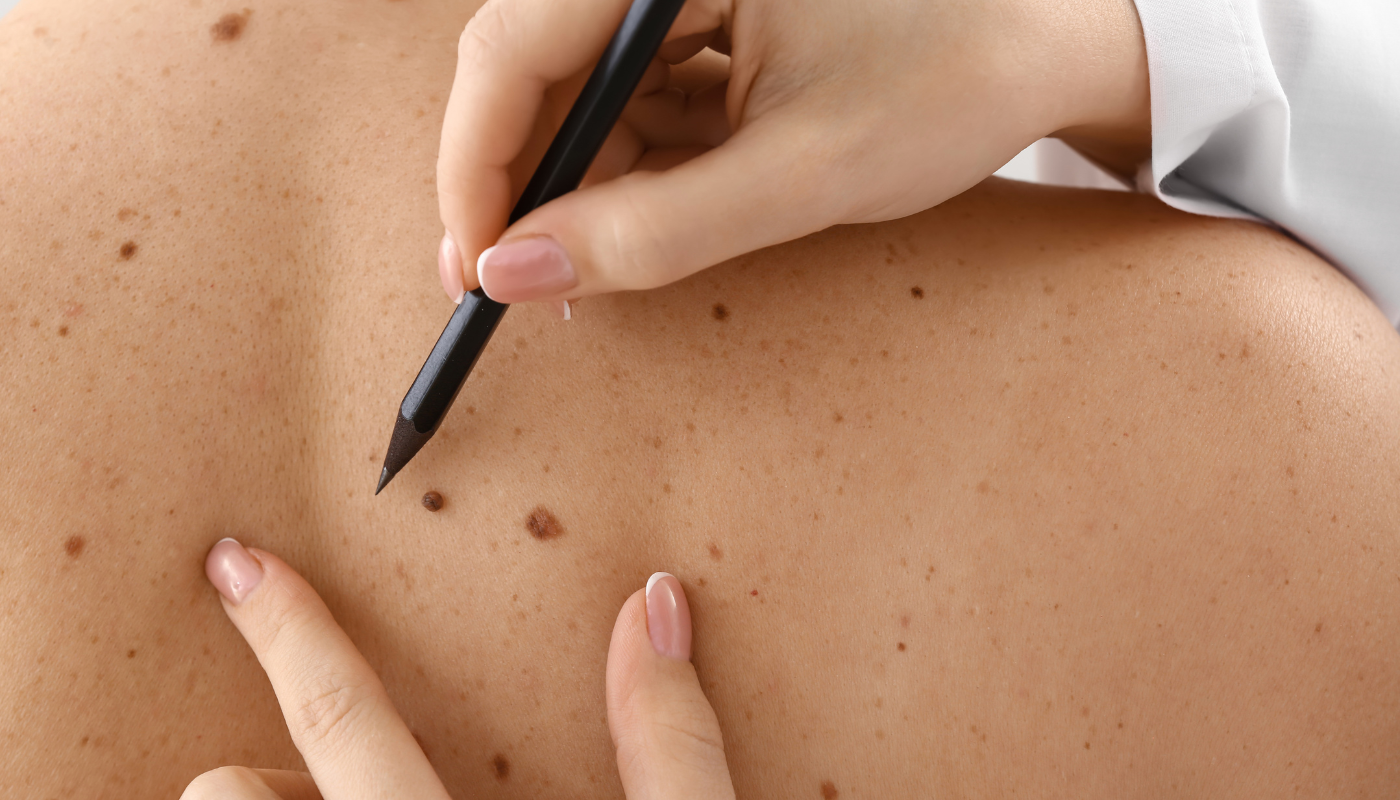

Skin cancer is one of the most common cancers globally, and among its many forms, melanoma is the most aggressive.
Within the melanoma category, nodular melanoma stands out as one of the most dangerous and fast-growing types. Because it doesn’t always follow the usual warning signs of skin cancer, it's crucial to understand what it looks like, how it behaves, and what risk factors contribute to its development.
In this article, we’ll explore in detail what nodular melanoma looks like, how you can identify it, and what causes it, so you can be proactive about your skin health.
What Does Nodular Melanoma Look Like?
Unlike many other types of melanoma, which begin as flat, irregular moles that slowly change over time, nodular melanoma often appears suddenly and grows rapidly. It is a raised, dome-shaped bump that may initially seem harmless—especially if it's flesh-coloured or similar to a pimple or bug bite.
Here are some of the key features of nodular melanoma:
- Shape and elevation: Typically raised and dome-shaped, nodular melanoma can be smooth to the touch or have a rough, crusty surface.
- Colour: It can be black, blue, red, or even skin-coloured, which can make it deceptively difficult to identify. Some may appear pink or reddish due to the blood vessels feeding the rapidly growing cancer cells.
- Surface changes: The lesion may ulcerate (form an open sore) or bleed, especially if irritated or scratched.
- Firmness: The bump is often firm to the touch, distinguishing it from softer, benign skin lumps like cysts.
- Rapid growth: One of the most notable features is how quickly it grows—weeks rather than months.
Because it grows down into the skin layers rather than spreading across the surface, nodular melanoma can go undetected until it becomes more serious.
This is why prompt identification is key.
How Can I Tell If a Mole Is Nodular Melanoma?
Most people are familiar with the ABCDE rule used to identify common melanomas:
- Asymmetry
- Border irregularity
- Colour variation
- Diameter over 6mm
- Evolution or change over time
However, nodular melanoma often doesn't follow this pattern.
It can look symmetrical, have regular borders, and appear small—yet still be highly dangerous.
Instead, nodular melanoma follows the EFG rule:
- Elevated – It sticks out above the skin surface.
- Firm – It feels solid and doesn’t move easily under pressure.
- Growing – It changes size noticeably and quickly, often over the course of a few weeks.
If you notice a new bump that’s growing fast, especially if it's unlike your other moles or skin lesions, it’s crucial to see a dermatologist without delay. Even if it’s not dark or irregular in colour, any unusual growth on your skin deserves medical attention—particularly if it's changing or bleeding.
Warning signs to watch for:
- A spot that wasn't there before and is getting bigger quickly
- A bump that feels hard and is not tender or painful
- A lesion that starts to bleed or scab for no clear reason
- A mole or bump that looks different from all others on your skin (“ugly duckling” sign)
Nodular melanoma is often misdiagnosed initially because of its atypical appearance.
Trust your instincts—if something looks or feels wrong, push for a second opinion or further testing.
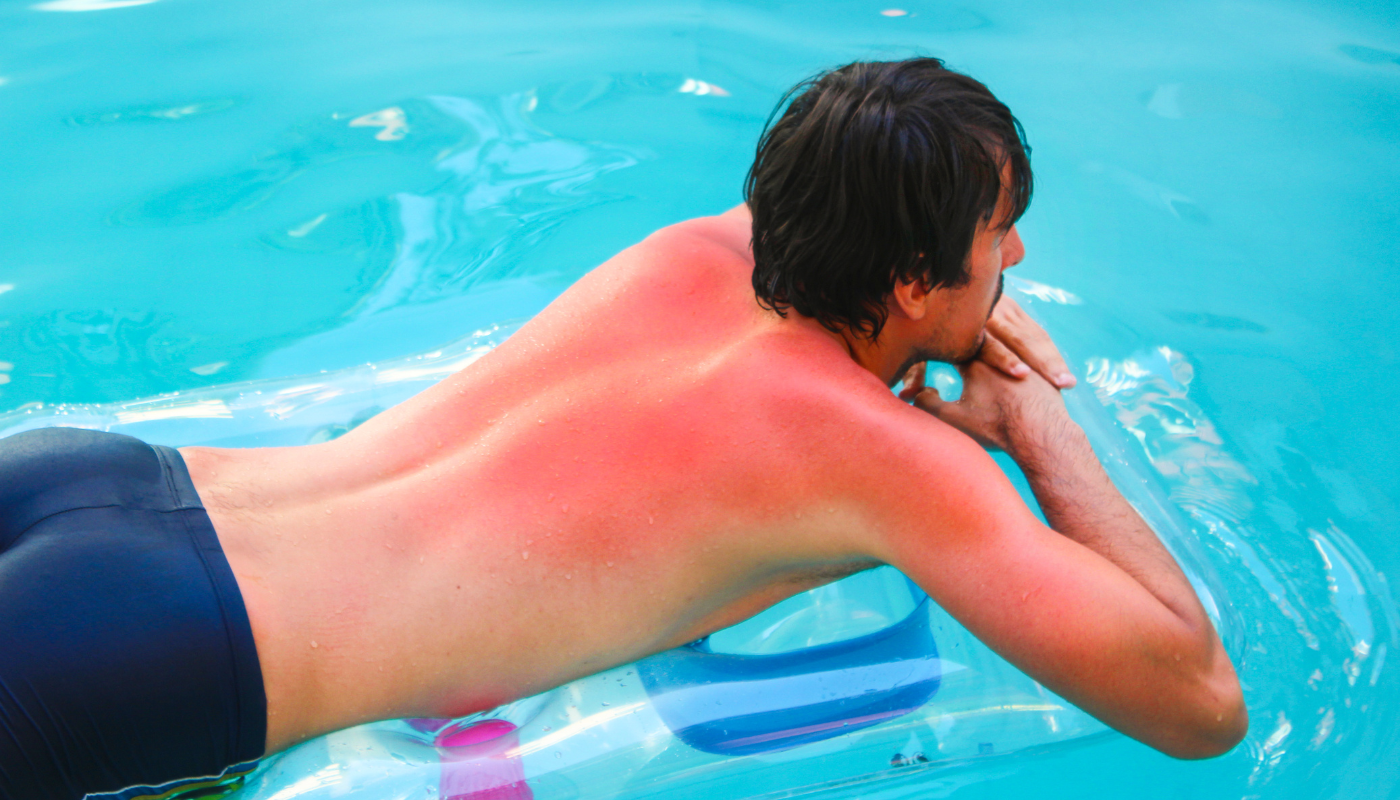

What Causes Nodular Melanoma?
Like all cancers, nodular melanoma results from mutations in cells—in this case, melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells of the skin. These mutations lead to uncontrolled cell growth and tumor formation.
While the exact cause of these mutations isn't always known, several well-established risk factors have been linked to the development of nodular melanoma.
1. Excessive UV Exposure
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds is one of the biggest risk factors for all types of melanoma, including nodular melanoma. UV light can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that trigger cancer.
- Repeated sunburns, especially blistering ones, are particularly harmful.
- People who spend a lot of time outdoors without sun protection or who use tanning beds are at increased risk.
2. Severe or Frequent Sunburns
A history of intense sun exposure, particularly during childhood or adolescence, increases the risk of developing melanoma later in life. Even one or two severe sunburns may significantly raise your lifetime risk.
3. Fair Skin and Light Features
People with fair skin, light eyes, and blonde or red hair are more vulnerable to UV damage because they have less melanin—the natural pigment that provides some protection from UV rays.
This doesn’t mean people with darker skin tones are immune, but their risk is comparatively lower.
4. Family History of Melanoma
If you have a first-degree relative (parent, sibling, or child) who has had melanoma, your risk is higher. This may be due to shared genetic mutations or common environmental factors.
5. Weakened Immune System
Individuals with a compromised immune system—due to organ transplants, HIV/AIDS, or immunosuppressive drugs—are more likely to develop skin cancers, including nodular melanoma.
6. Moles and Atypical Nevi
Having many moles (more than 50), or atypical moles (dysplastic nevi), increases your risk. Even if nodular melanoma often arises from normal-looking skin, people with lots of moles should still be on high alert for changes.
7. Nodular Melanoma Can Appear in Hidden Areas
One particularly dangerous aspect of nodular melanoma is that it can appear in places not typically exposed to the sun, such as the scalp, under the nails, or on mucosal surfaces. This is in contrast to other melanomas, which are usually more common on sun-exposed areas.
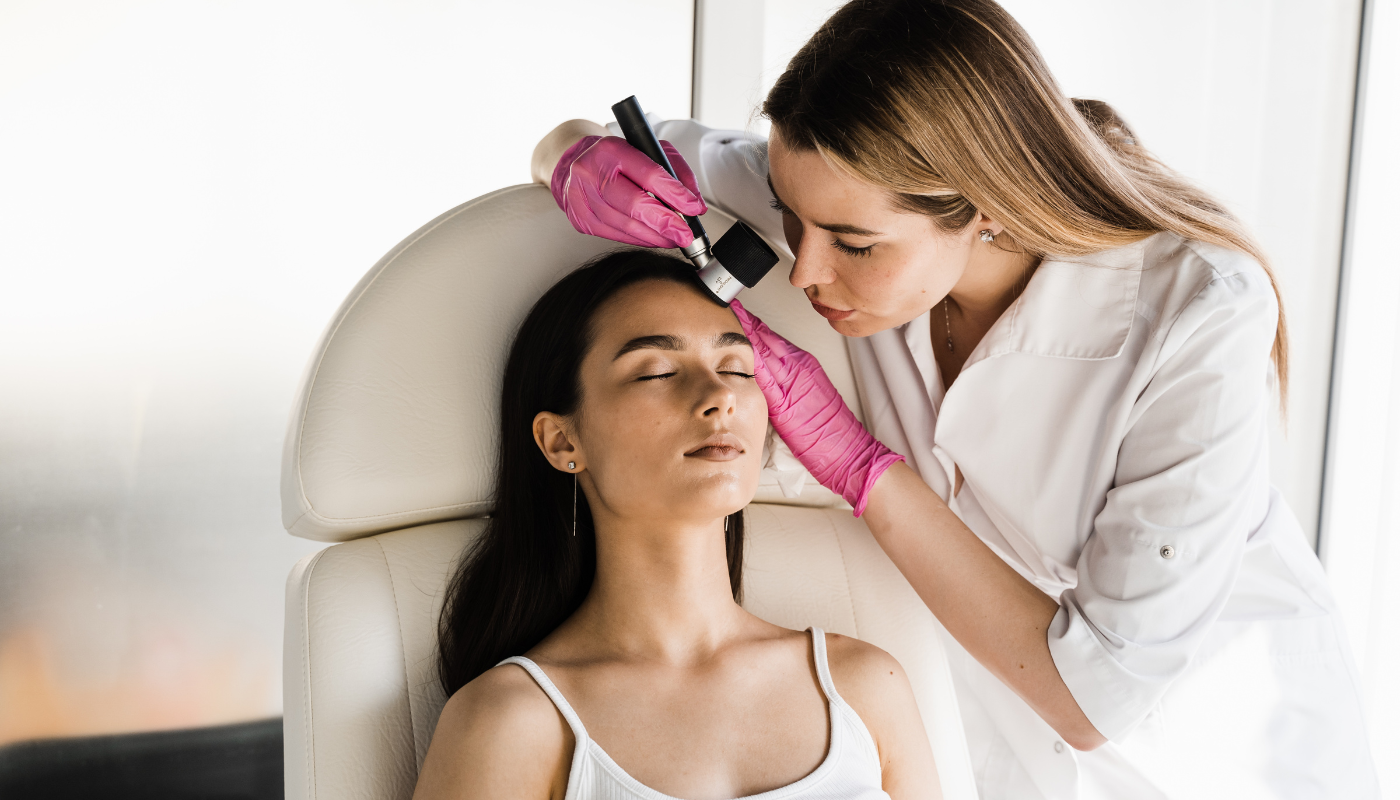
For this reason, it’s important to regularly check your entire body, not just your arms and face. Ask your doctor to do a full-body skin check at least once a year, or more often if you’re at high risk.
Why Is Nodular Melanoma So Dangerous?
Nodular melanoma accounts for about 15% of melanoma cases, but it is responsible for a disproportionately high number of melanoma-related deaths.
Why? Because it grows fast and often goes unnoticed until it has already spread (metastasized) to other parts of the body.
Key reasons it’s so dangerous:
- Rapid growth: It grows vertically into the skin rather than horizontally across the surface, making it more likely to spread quickly to lymph nodes or internal organs.
- Difficult detection: It often appears as a new bump, not a changing mole, so people may dismiss it as harmless.
- Atypical appearance: Its colour and shape don’t always look suspicious, so diagnosis may be delayed.
Early detection is absolutely vital. If caught early, melanoma can often be cured with surgical removal.
But once it spreads, treatment becomes more complex and outcomes less certain.
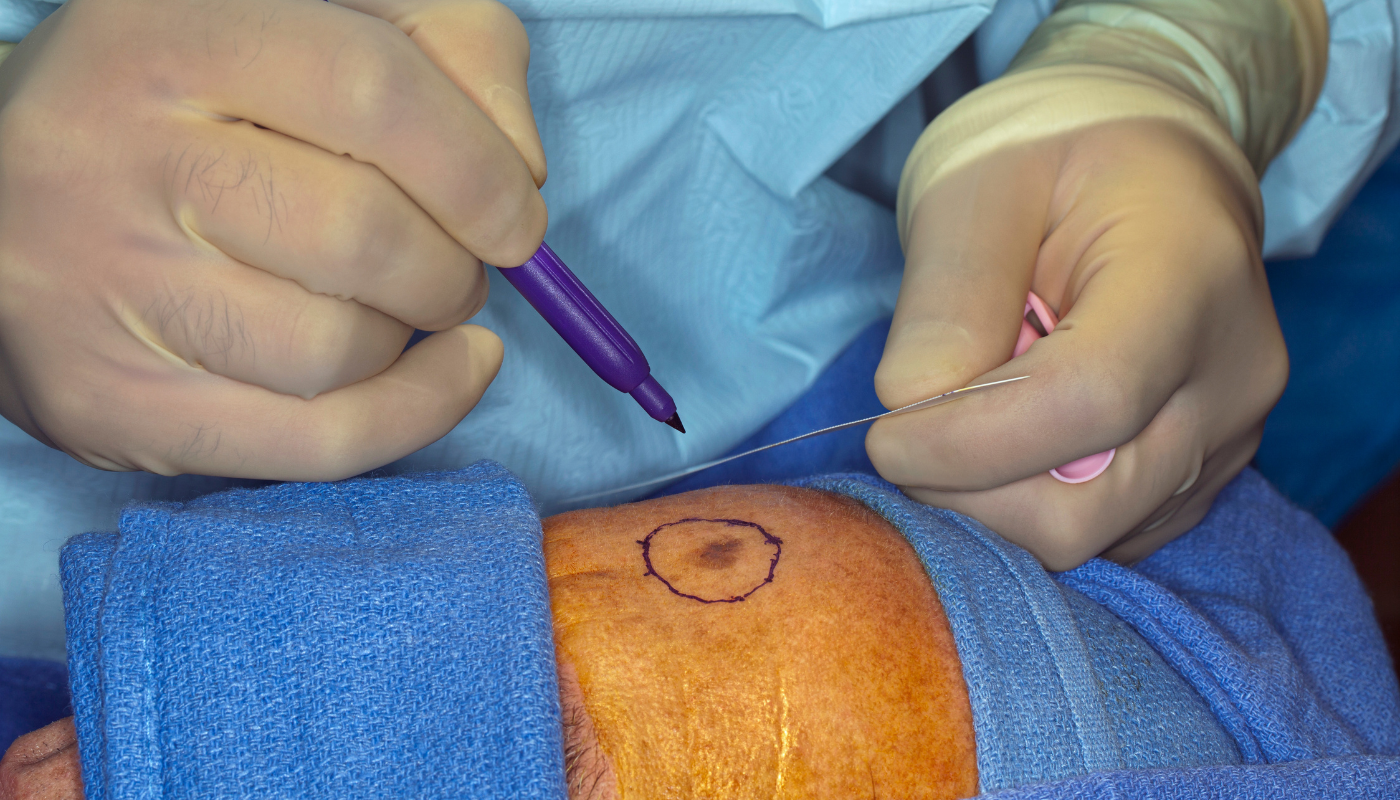
How Is Nodular Melanoma Diagnosed and Treated?
If your doctor suspects a lesion might be melanoma, the first step is usually a skin biopsy, where a sample of the tissue is removed and examined under a microscope.
If confirmed as nodular melanoma, treatment may include:
- Surgical excision: Removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue.
- Lymph node biopsy: To check if the cancer has spread.
- Immunotherapy: Medications that help your immune system attack cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: For melanomas with certain genetic mutations (like BRAF).
- Radiation or chemotherapy: Less commonly used, but may be part of advanced treatment plans.
Protecting Yourself: Prevention and Monitoring
Sun safety tips:
- Use sunscreen with SPF 30+ every day, even on cloudy days.
- Wear protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses.
- Avoid tanning beds entirely.
- Seek shade during peak sunlight hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
Skin monitoring tips:
- Perform monthly skin self-checks, examining every part of your body.
- Take photos of moles or bumps to track changes over time.
- If you notice something new, firm, and fast-growing,
don’t delay—get it checked.
Conclusion
Nodular melanoma is a silent threat that doesn’t always look suspicious.
Unlike traditional melanomas that develop slowly and follow the ABCDE rules, nodular melanoma grows rapidly and often disguises itself as a harmless bump.
By understanding what nodular melanoma looks like—raised, firm, and growing—you can catch it earlier and improve your chances of successful treatment.
Be proactive about your skin health, protect yourself from excessive UV exposure, and seek medical advice for anything unusual. Early detection saves lives.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. If you have concerns about your skin or notice unusual changes, consult a qualified healthcare professional.
More Skin Tips.
CoreBodi








| Powered by Kaptol Media


