Understanding the Sun Protection Factor (SPF) Scale
Understanding the Sun Protection Factor (SPF) Scale: Why High SPF Sunscreen is Essential for Skin Cancer Prevention

The sun is a source of life, providing warmth and essential vitamin D.
However, prolonged and unprotected exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation poses serious risks to skin health.
From sunburn and premature aging to an increased likelihood of skin cancer, UV rays can cause irreversible damage.
This is where sunscreen, specifically those with high Sun Protection Factor (SPF), plays a crucial role in safeguarding skin health.
What is SPF and How Does it Work?
Sun Protection Factor (SPF) is a crucial measure of how effectively a sunscreen can shield the skin from harmful ultraviolet B (UVB) rays. UVB rays are primarily responsible for causing sunburn and are a major factor in the development of skin cancer. When applied correctly, sunscreen with SPF helps reduce the risk of sun damage, premature aging, and other harmful effects of prolonged sun exposure.
How SPF Works
The SPF number represents how long a person can be exposed to UVB rays before experiencing sunburn, compared to unprotected skin. For example, if your skin would normally burn after 10 minutes in the sun, applying an SPF 30 sunscreen theoretically extends that time by 30 times, meaning it would take approximately 300 minutes (or five hours) for the same level of redness to occur.
However, real-world factors such as sweating, swimming, and inadequate application can reduce effectiveness, making frequent reapplication essential.
SPF Protection Levels
While a higher SPF does provide more protection, the increase in protection is not linear:
- SPF 15: Blocks about 93% of UVB rays.
- SPF 30: Blocks about 97% of UVB rays.
- SPF 50: Blocks around 98% of UVB rays.
- SPF 100: Blocks about 99% of UVB rays.
It’s important to note that no sunscreen can block 100% of UV rays. The difference in UVB protection between SPF 30 and SPF 50 is only about 1%, yet SPF 50 provides better protection for longer periods.
SPF and UVA Protection
SPF ratings only measure protection against UVB rays. However, UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin, contributing to premature aging and increasing the risk of skin cancer. To ensure full-spectrum protection, look for sunscreens labeled “broad-spectrum,” which means they shield against both UVA and UVB radiation.
The Benefits of Using High SPF Sunscreen
Using a high SPF sunscreen provides significant advantages, particularly for people with fair skin, those with a history of skin cancer, or anyone spending extended periods outdoors.
Here are some key benefits:
1. Enhanced UVB Protection
High SPF sunscreens provide a greater level of protection against harmful UVB rays, reducing the risk of sunburn and preventing immediate skin damage.
2. Greater Margin for Application Errors
Most people do not apply enough sunscreen to achieve the full protection stated on the label. High SPF sunscreen helps compensate for this, ensuring better coverage and longer protection even when application is not perfect. (Skin Cancer Foundation)
3. Essential for Sensitive or High-Risk Individuals
People with fair skin, a history of skin cancer, or certain medical conditions that increase sun sensitivity benefit more from using a high SPF sunscreen, as it offers stronger protection.
4. Protection Against Premature Aging
Sun exposure leads to photoaging, causing wrinkles, fine lines, and dark spots. Regular application of high SPF sunscreen slows down premature aging and maintains youthful, healthy skin. (American Academy of Dermatology)

Sunscreen and Skin Cancer Prevention
Skin cancer is the most common cancer worldwide, with melanoma being the deadliest form.
Excessive UV exposure is a leading cause of skin cancer.
Regular sunscreen use, particularly with SPF 30 or higher, has been scientifically proven to reduce the risk of skin cancer. (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
How Sunscreen Prevents Skin Cancer:
- Melanoma Prevention: Studies indicate that using SPF 15 or higher regularly reduces the risk of developing melanoma by 50%.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prevention: Sunscreen has been shown to decrease the risk of squamous cell carcinoma by about 40%.
Choosing the Right Sunscreen
When selecting sunscreen, consider the following factors:
1. Broad-Spectrum Protection
A broad-spectrum sunscreen protects against both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays contribute to aging and skin cancer, while UVB rays cause sunburn and DNA damage.
2. SPF 30 or Higher
Dermatologists recommend using SPF 30 or higher for adequate protection, especially for prolonged outdoor activities.
3. Water Resistance
For swimming or sweating, choose a water-resistant sunscreen that offers protection for 40 to 80 minutes before needing reapplication.
4. Suitable for Your Skin Type
- For sensitive skin: Opt for mineral-based sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide.
- For oily or acne-prone skin: Choose non-comedogenic, oil-free formulas.
- For dry skin: Look for sunscreens with added moisturizing ingredients like hyaluronic acid or glycerin.

Proper Sunscreen Application for Maximum Protection
To ensure sunscreen works effectively, follow these application tips:
- Apply Generously: Use one ounce (a shot glass full) for full-body coverage.
- Apply 15-30 Minutes Before Sun Exposure: Sunscreen takes time to absorb and provide protection.
- Reapply Every Two Hours: Sunscreen effectiveness decreases over time, especially when swimming or sweating.
- Don’t Miss Key Areas: Cover ears, neck, tops of feet, and scalp if exposed.
Common Myths and Misconceptions About Sunscreen
1. “Higher SPF Means I Can Stay in the Sun All Day”
Even high SPF sunscreens require reapplication every two hours. Extended exposure without reapplying increases skin cancer risk.
2. “Darker Skin Doesn’t Need Sunscreen”
While melanin provides some natural UV protection, darker skin tones can still experience sun damage and skin cancer. Sunscreen is essential for everyone. (American Cancer Society)
3. “A Base Tan Protects Against Sunburn”
A tan is a sign of skin damage, not protection. Any change in skin color from UV exposure indicates DNA damage.
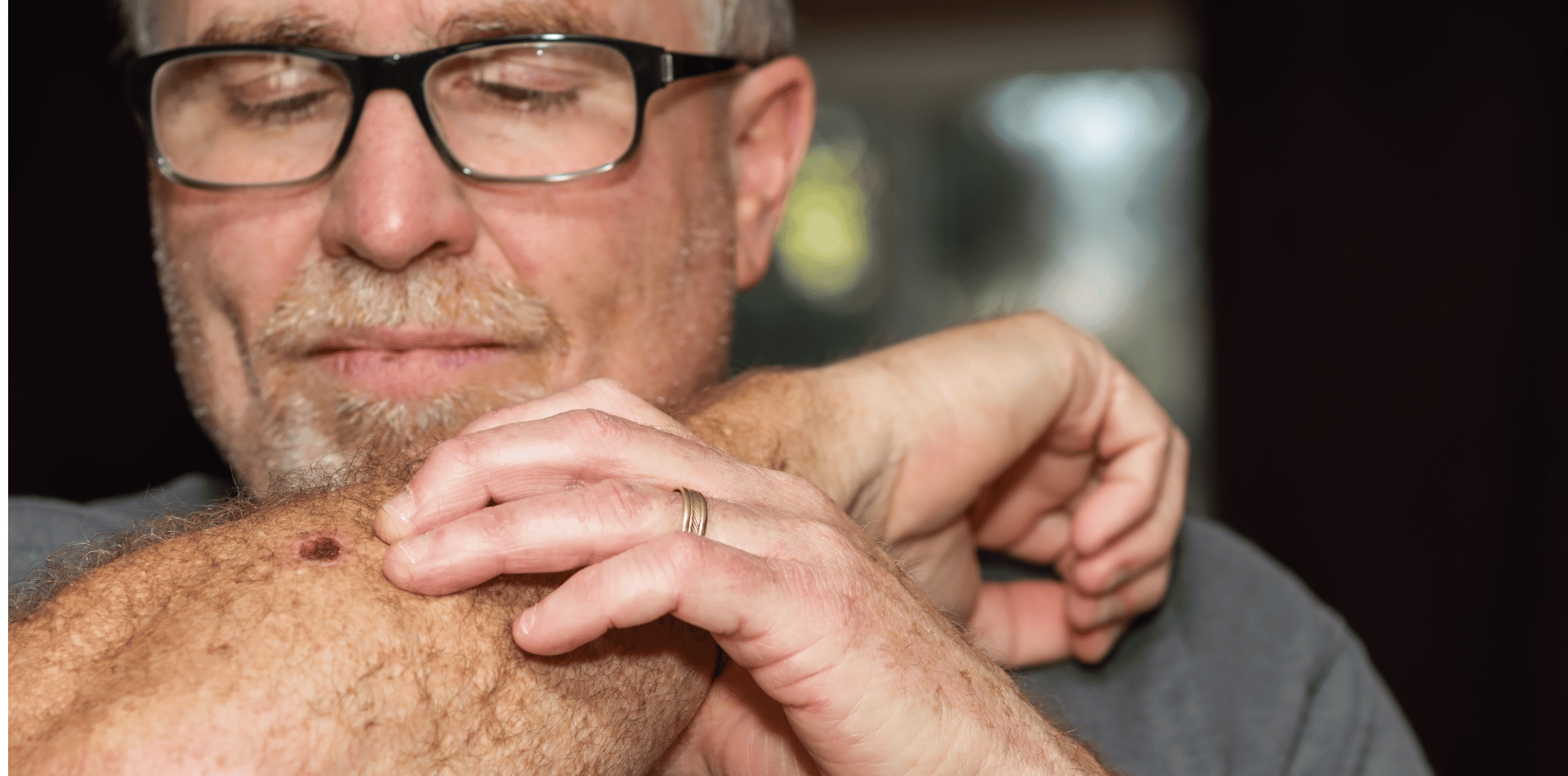
Final Thoughts: Prioritize Sun Safety
Using a high SPF sunscreen is one of the most effective ways to protect against sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer.
However, it should be combined with other sun-protection strategies, such as wearing protective clothing, sunglasses, and seeking shade when UV levels are high.
By understanding the importance of SPF and incorporating daily sunscreen use into your routine, you can significantly reduce your risk of sun-related skin damage and maintain healthy skin for years to come.
Further Reading:
More Skin Tips.
CoreBodi







| Powered by Kaptol Media


