Skin Cancer verses Age Spots
Skin Cancer verses Age Spots
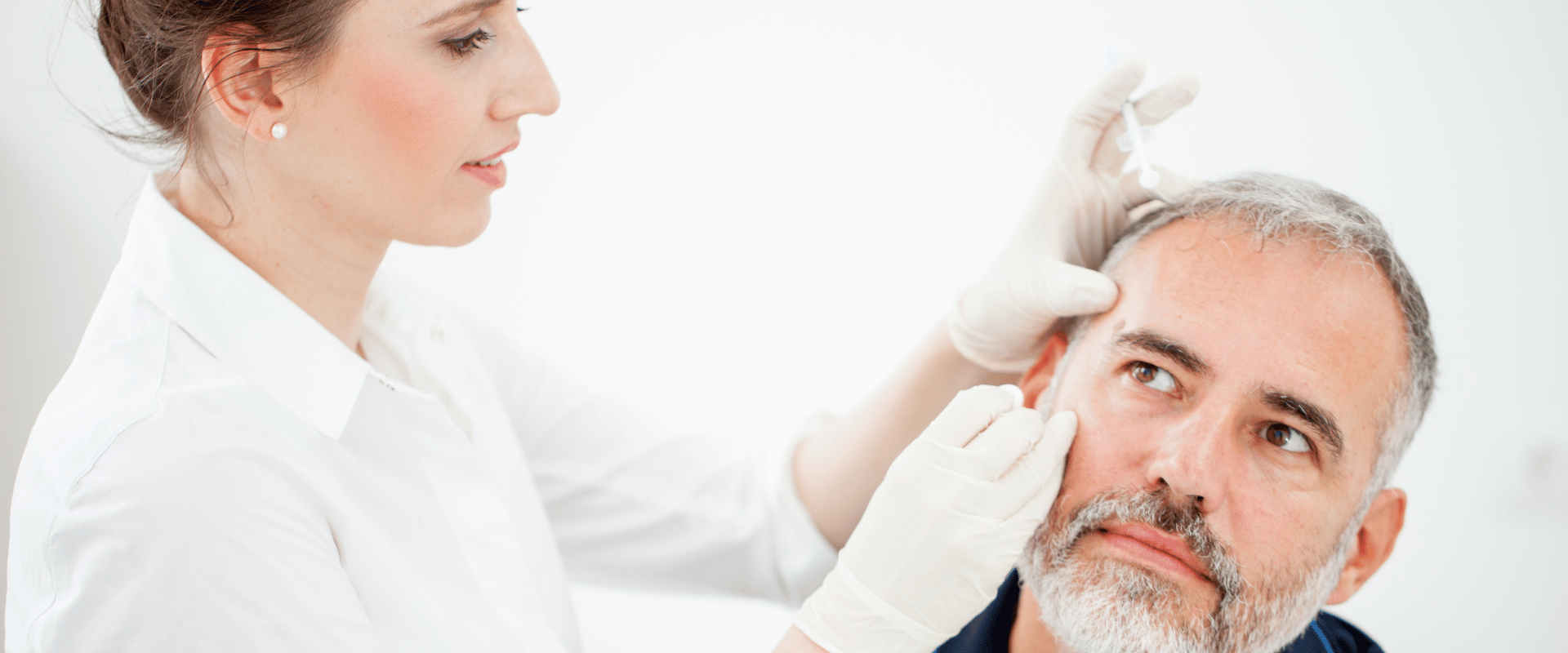
Skin-related concerns can be a cause for worry, especially when it comes to distinguishing between harmless conditions like age spots and potentially serious conditions like skin cancer. While age spots and skin cancer may appear similar in some aspects, they differ significantly in terms of causes, characteristics, and potential risks.
In this article, we will delve into the distinctions between these two conditions, shedding light on their causes, symptoms, and appropriate courses of action.
Understanding Age Spots:
Age spots, also known as liver spots or solar lentigines, are benign skin discolourations that commonly occur in older adults.
They typically appear as small, flat patches of hyperpigmentation on areas of the body frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, shoulders, and arms. Age spots are caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds over the years. This exposure triggers an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin coloration, leading to the formation of darker patches.
Age spots are typically harmless and do not require medical treatment.
They do not pose any immediate health risks and are primarily a cosmetic concern.
However, individuals with age spots should still take precautionary measures to protect their skin from further sun damage and prevent the development of other skin conditions.
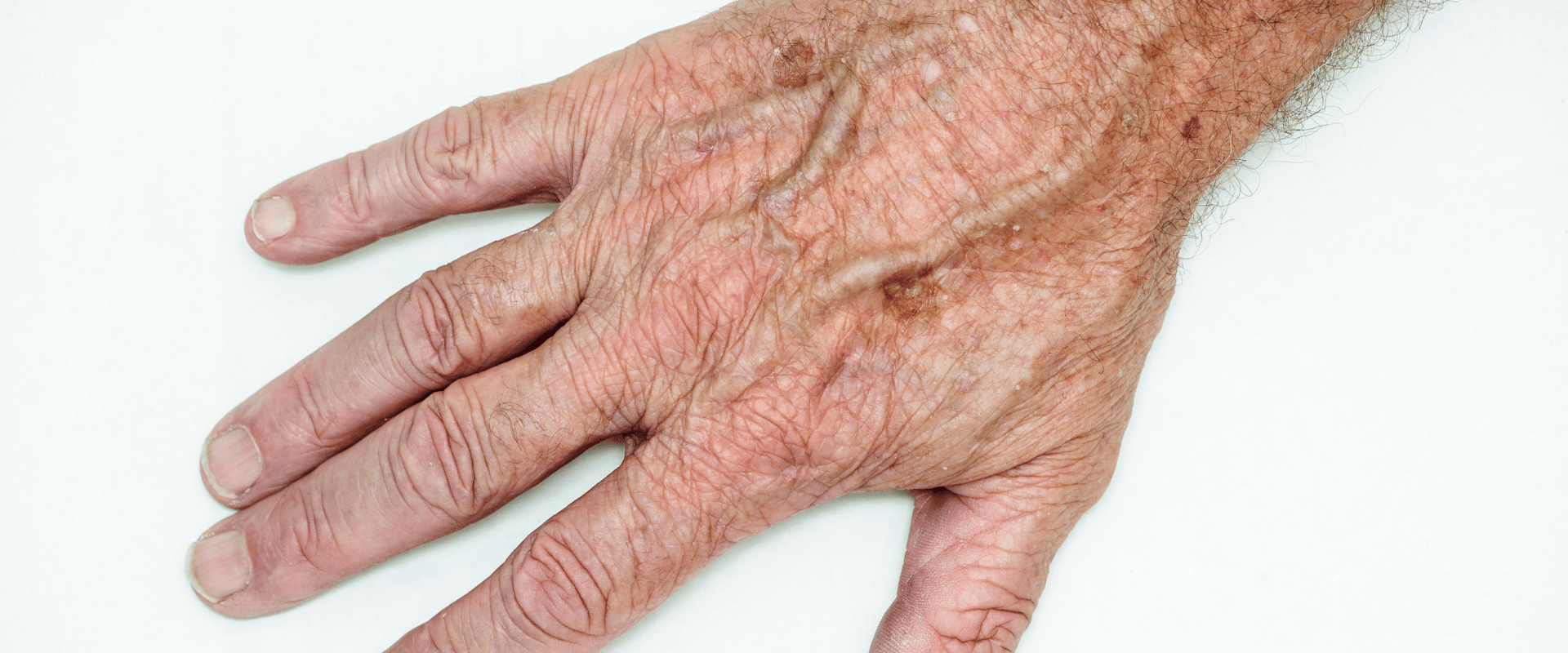
Distinguishing Characteristics of Age Spots:
- Appearance: Age spots are usually flat, round or oval-shaped patches with well-defined borders. They are typically brown, tan, or black in colour and range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters.
- Texture: Age spots are smooth to the touch and do not cause any physical discomfort, such as itching or pain.
- Location: They tend to appear on areas that receive the most sun exposure, such as the face, hands, shoulders, and arms.
- Stability: Age spots generally remain stable in size, colour, and shape over time. They do not exhibit rapid growth or changes.
Understanding Skin Cancer:
Skin cancer, on the other hand, is an abnormal growth of skin cells that can have potentially serious implications.
It develops when the DNA within skin cells becomes damaged, typically due to prolonged exposure to UV radiation.
There are different types of skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
While each type has distinct characteristics and behaviors, all forms of skin cancer should be taken seriously and addressed promptly.
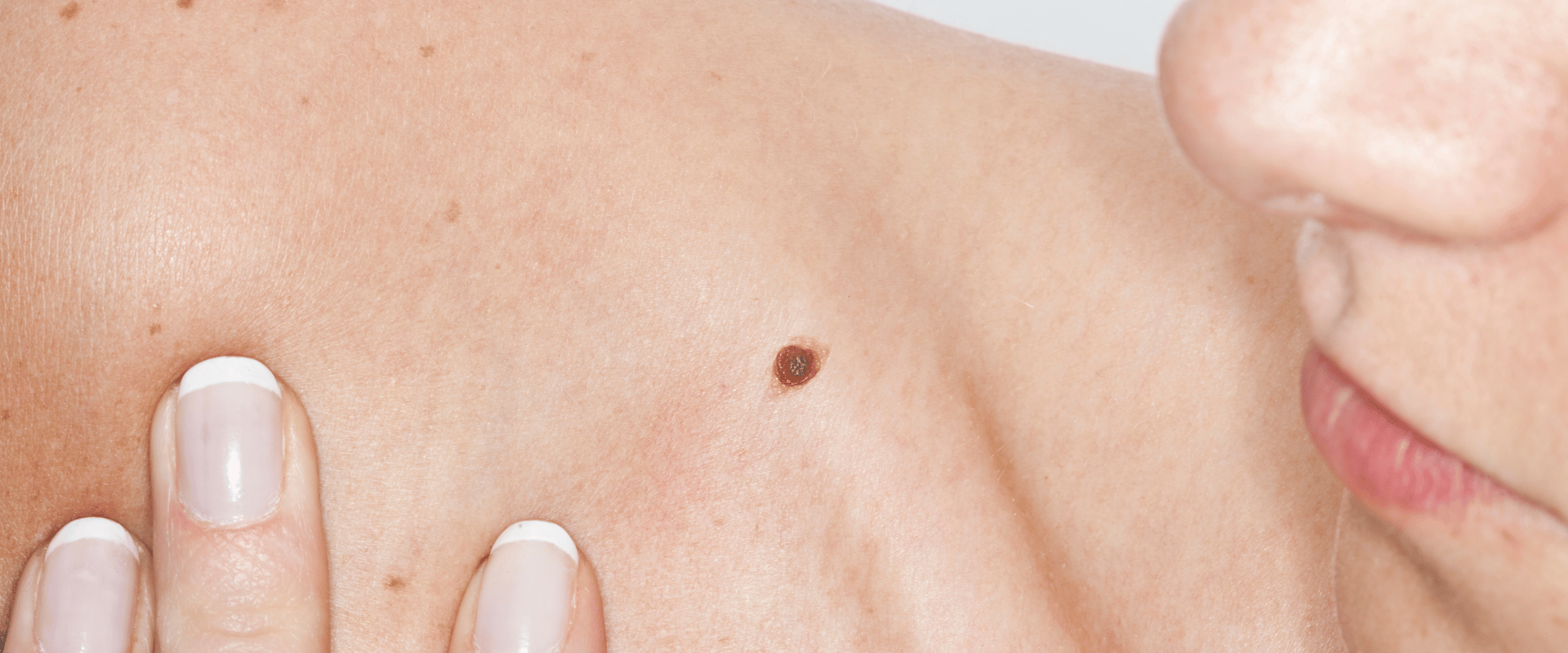
Distinguishing Characteristics of Skin Cancer:
- Appearance: Skin cancer can manifest in various ways, ranging from irregularly shaped moles or sores to pink or red patches on the skin. Basal cell carcinomas often appear as raised, pearly bumps, while squamous cell carcinomas may present as scaly or crusty lesions. Melanomas, the most dangerous form of skin cancer, can exhibit irregular borders, multiple colours, and asymmetrical shapes.
- Texture: Unlike age spots, skin cancer lesions may exhibit changes in texture, such as becoming scaly, crusty, or bleeding easily.
- Location: Skin cancer can occur anywhere on the body, even in areas that receive minimal sun exposure. It can develop on sun-exposed areas like the face, neck, arms, and legs, but it can also appear on covered areas or mucous membranes.
- Changes Over Time: Skin cancer lesions may undergo changes over time, including growth in size, changes in colour, or the appearance of new symptoms like itching, bleeding, or tenderness.
Risk Factors and Prevention:
Age spots and skin cancer differ significantly in terms of risk factors and preventive measures.
Risk Factors for Age Spots:
Age: Age spots are more prevalent in individuals over the age of 50, although they can occur at any age.
Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to the sun or tanning beds without adequate protection increases the likelihood of developing age spots.
Preventive Measures for Age Spots:
Sun Protection: Wearing protective clothing, applying sunscreen with a high SPF, and seeking shade during peak sun hours can help prevent the formation of age spots.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer:
- Sun Exposure: Extensive exposure to UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds is the primary risk factor for skin cancer.
- Fair Skin: People with fair skin, light-coloured hair, and light-coloured eyes are at a higher risk due to reduced melanin levels and decreased natural sun protection.
- Family History: A family history of skin cancer increases an individual's susceptibility to the disease.
- Immunosuppression: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as organ transplant recipients or those with HIV/AIDS, have an elevated risk of developing skin cancer.

Preventive Measures for Skin Cancer:
- Sun Protection: Regularly applying broad-spectrum sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, using sunglasses, and seeking shade can significantly reduce the risk of skin cancer.
- Regular Skin Examinations: Periodic self-examinations of the skin and annual professional skin checks can help detect skin cancer at its early stages.
Conclusion:
Differentiating between age spots and skin cancer is crucial for individuals to take appropriate action and seek necessary medical attention. While age spots are benign and primarily a cosmetic concern, skin cancer poses a significant health risk that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the distinctions in their characteristics, risk factors, and preventive measures empowers individuals to protect their skin health and seek timely medical intervention when needed. Regular skin self-examinations, sun protection practices, and consultation with healthcare professionals play key roles in maintaining healthy skin and reducing the risk of skin cancer.
More Skin Tips.
CoreBodi







| Powered by Kaptol Media


