Understanding Skin Cancer: Types, Causes, and Risk Factors
Understanding Skin Cancer: Types, Causes, and Risk Factors
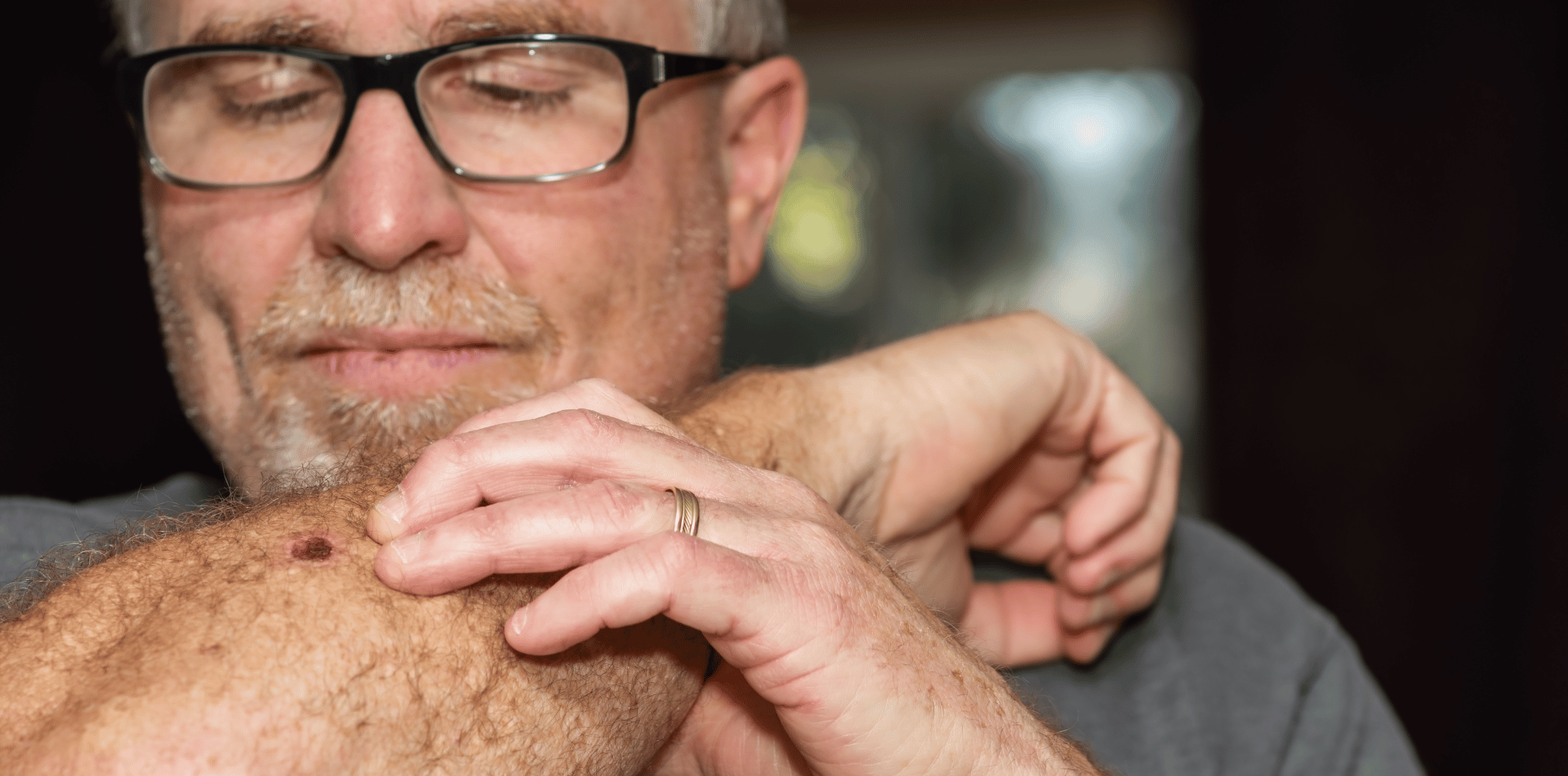
Skin cancer is a prevalent and potentially deadly disease that affects millions of people worldwide.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the various aspects of skin cancer, from its types and causes to the risk factors associated with it.
Read this to the end and you will have a deeper understanding of this disease, its potential causes, and what you can do to protect yourself.
Types of Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basal Cell Carcinoma, or BCC, is one of the most common types of skin cancer.
It often appears as a small, shiny bump or a red patch, and it usually occurs in areas frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face and neck. BCC tends to grow slowly and rarely metastasizes to other parts of the body. Nevertheless, it should not be taken lightly, as it can cause disfigurement if left untreated.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Squamous Cell Carcinoma, or SCC, is another prevalent form of skin cancer.
Unlike BCC, SCC has a higher potential to spread to nearby tissues if not treated promptly. It often appears as a red, scaly patch or a sore that does not heal. SCC is commonly found on sun-exposed areas like the ears, face, and hands.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer due to its ability to spread rapidly to other parts of the body.
It usually develops from melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the skin. Melanoma often presents as an irregularly shaped mole or dark spot with uneven borders and varying colors.
Early detection and treatment are crucial in managing melanoma.
Causes of Skin Cancer
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation
UV radiation from the sun and artificial sources, such as tanning beds, is a leading cause of skin cancer.
Prolonged exposure to UV rays can damage the DNA in your skin cells, increasing the risk of cancer development. It's essential to protect your skin from excessive UV radiation by using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade when necessary.
Genetic Factors
Genetics can play a significant role in your risk of developing skin cancer.
If you have a family history of the disease, you may be genetically predisposed to it.
Genetic testing can help determine your susceptibility and guide preventive measures and screening schedules.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, including exposure to certain chemicals and pollutants, can increase your risk of skin cancer.
Occupational exposure to carcinogens, such as arsenic or coal tar, can elevate your susceptibility.
Additionally, living in areas with higher levels of air pollution may also contribute to skin cancer risk.
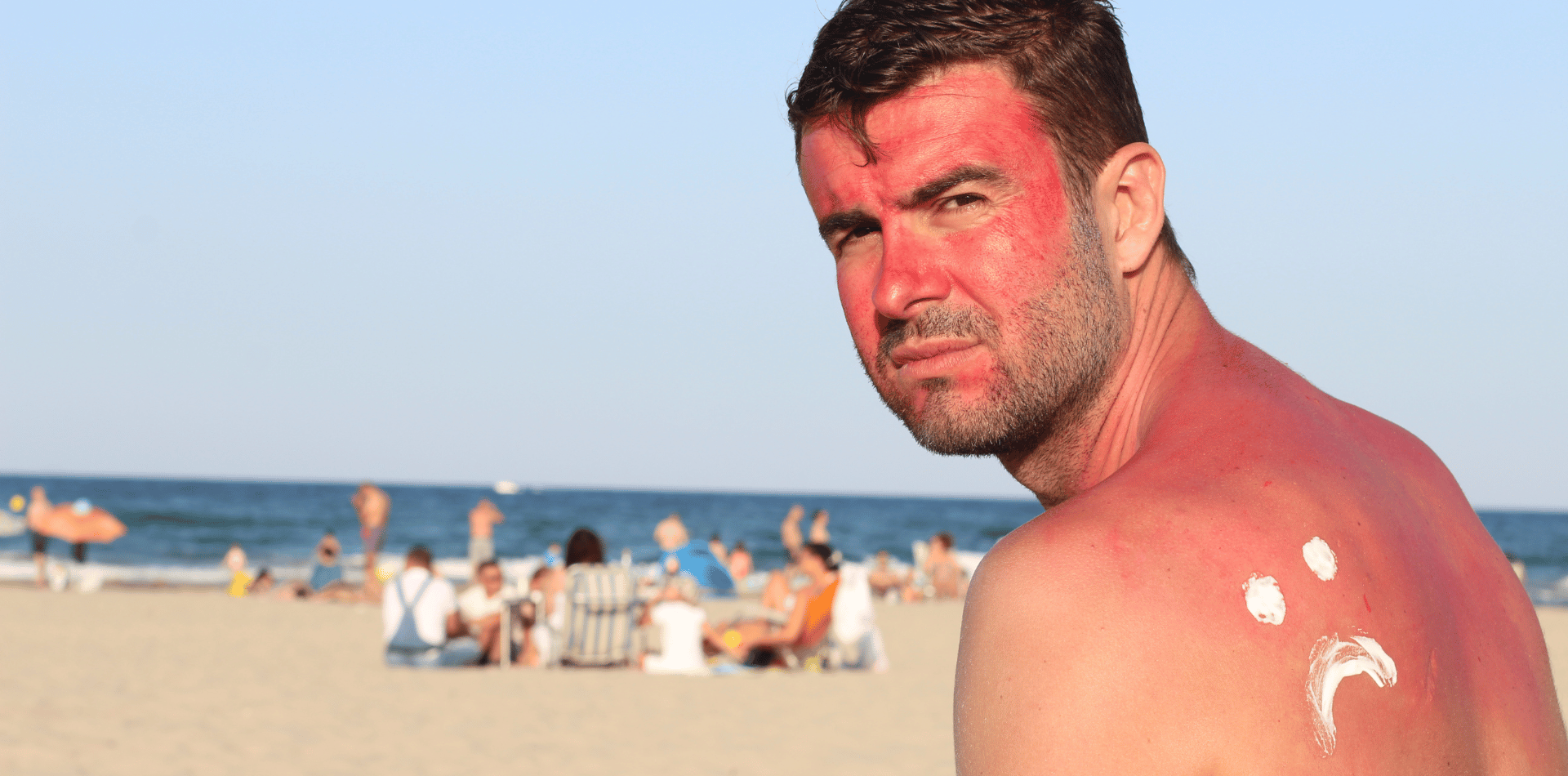

Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
Fair Skin and Sun Sensitivity
People with fair skin, who sunburn easily and have less melanin, are more susceptible to skin cancer.
The Fitzpatrick scale categorizes skin types, with fair-skinned individuals typically falling into the higher risk categories.
Sun Exposure
Cumulative sun exposure over your lifetime can significantly impact your risk of skin cancer.
Outdoor activities and occupations that involve prolonged sun exposure, such as farming or construction work, can increase your vulnerability.
Age and Gender
Skin cancer risk increases with age, and men are generally at a higher risk than women.
However, skin cancer can affect individuals of all ages and genders.
Young people may develop atypical cases, emphasising the importance of vigilance and early detection.
Prevention and Early Detection
Sun Safety Measures
Protecting your skin from UV radiation is crucial in preventing skin cancer.
Use sunscreen with a high SPF, wear wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and protective clothing, and seek shade during peak sunlight hours.
Self-Examination
Regular self-skin examinations can aid in early detection.
Check your skin for any changes, including new moles, changes in existing moles, or any abnormal growths.
If you notice anything suspicious, consult a dermatologist promptly.
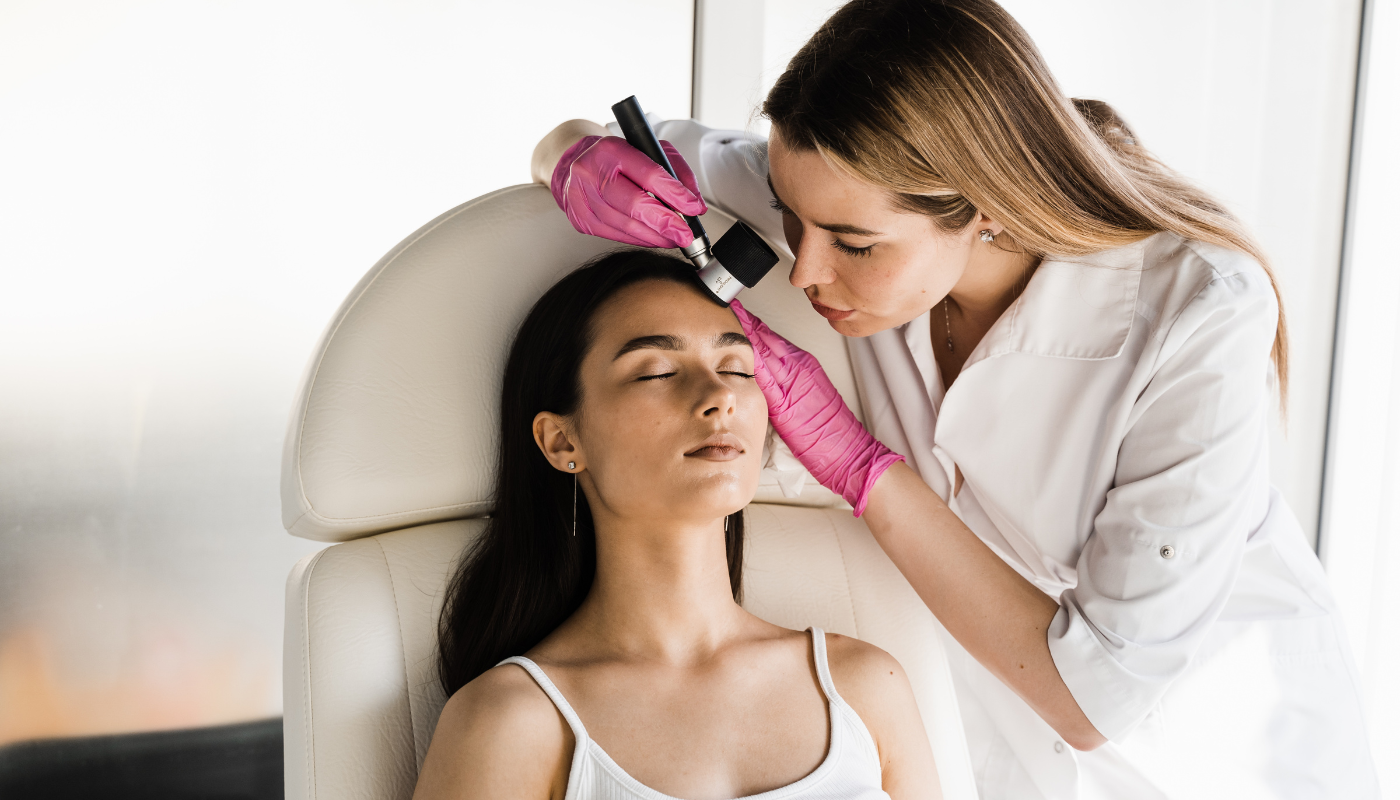
Medical Screening
Regular dermatological check-ups are essential, especially if you have risk factors or a family history of skin cancer.
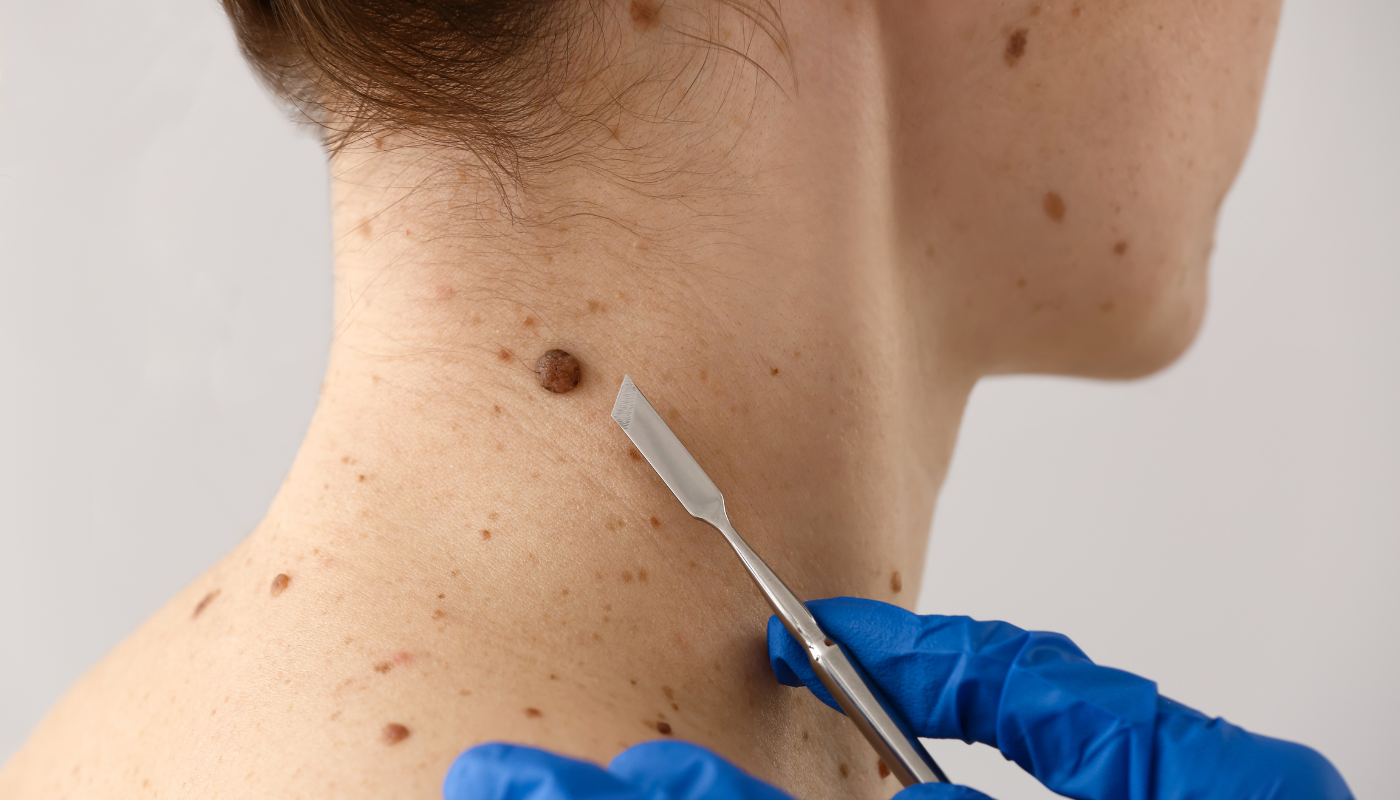
Dermatologists can perform skin examinations and recommend biopsies or other diagnostic procedures when necessary.
Treatment and Prognosis
Treatment Options
Treatment for skin cancer varies depending on the type and stage of the disease.
Options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy.
Emerging treatments and participation in clinical trials are also possibilities.
Prognosis Factors
The prognosis for skin cancer depends on several factors, including the type, stage, and early detection.
Survival rates vary, with early detection generally associated with better outcomes.
It's essential to discuss your prognosis and treatment options with your healthcare team.

Skin Cancer Awareness and Prevention
In conclusion, understanding the various types of skin cancer, their causes, and the associated risk factors is crucial in taking proactive steps to protect your skin health.
Skin cancer is a highly preventable and treatable disease when detected early.
By adopting sun safety measures, practicing self-examinations, and seeking regular medical screening, you can significantly reduce your risk and ensure early intervention if needed.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is skin cancer hereditary?
- While genetics can play a role in your susceptibility to skin cancer, it is not solely hereditary. Family history is a risk factor, but sun exposure and other environmental factors also contribute.
How often should I have a skin examination?
- The frequency of skin examinations depends on your risk factors and personal history. Generally, people with a higher risk should have annual exams, while others may opt for biennial or less frequent screenings.
Can skin cancer be completely cured?
- Skin cancer can often be completely cured, especially when detected and treated early. However, the prognosis depends on the type and stage of the cancer, so early detection is crucial.
What should I do if I notice a suspicious mole or growth?
- If you notice any changes in your skin, such as a new mole, changes in an existing mole, or any abnormal growth, consult a dermatologist promptly. They can assess the lesion and recommend appropriate steps, which may include a biopsy.
By staying informed, practicing sun safety, and being proactive about your skin health, you can significantly reduce your risk of skin cancer and ensure a healthier future for yourself and your loved ones.
More Skin Tips.
CoreBodi







| Powered by Kaptol Media


