Understanding The Risk Factors of Skin Cancer
Understanding the Risk Factors of Skin Cancer
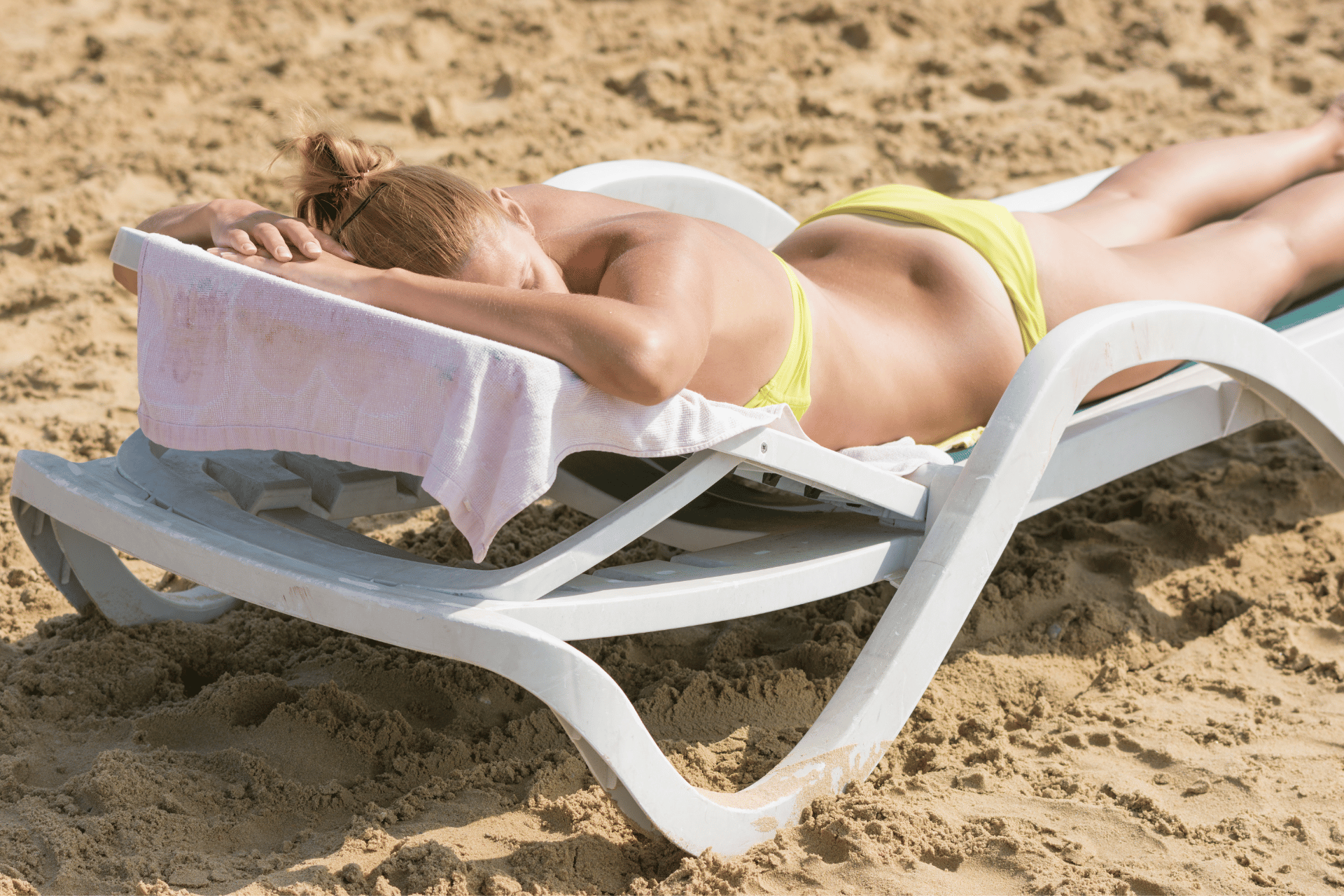

Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide, with millions of cases diagnosed every year.
It primarily affects the skin's outermost layer, and while anyone can develop skin cancer, certain individuals are at a higher risk than others. In this article, we will explore the key factors that contribute to the likelihood of developing skin cancer.
Sun Exposure:
Excessive exposure to the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the primary cause of skin cancer.
Individuals who spend prolonged periods in the sun without protection, such as sunscreen or protective clothing, are at a higher risk.
This includes people who work outdoors, sunbathe frequently, or participate in outdoor sports without proper precautions.
Fair Skin:
People with fair or light skin have less melanin, the pigment responsible for protecting the skin against UV damage. As a result, they are more susceptible to sunburns and have a higher risk of developing skin cancer.
This includes individuals with red or blonde hair, blue or green eyes, and numerous freckles or moles.
Family History:
A family history of skin cancer can significantly increase an individual's susceptibility to the disease. Certain inherited genetic mutations, such as those in the CDKN2A or p53 genes, can raise the risk of developing skin cancer. Therefore, individuals with a family history of the disease should be particularly vigilant in protecting their skin.
Age:
While skin cancer can affect people of any age, it becomes more prevalent as we grow older. This is partly due to accumulated exposure to UV radiation over time.
Additionally, older individuals may have a compromised immune system, making them more susceptible to skin cancer.
Weakened Immune System:
People with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing organ transplants, individuals with HIV/AIDS, or those taking immunosuppressant medications, are more susceptible to developing skin cancer.
A weakened immune system may struggle to combat cancerous cells, allowing them to proliferate more easily.
Previous Skin Cancer:
If an individual has previously been diagnosed with skin cancer, they are at a higher risk of developing the disease again. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals with a history of skin cancer to regularly monitor their skin, undergo follow-up examinations, and take preventive measures to reduce the chances of recurrence.
Conclusion:
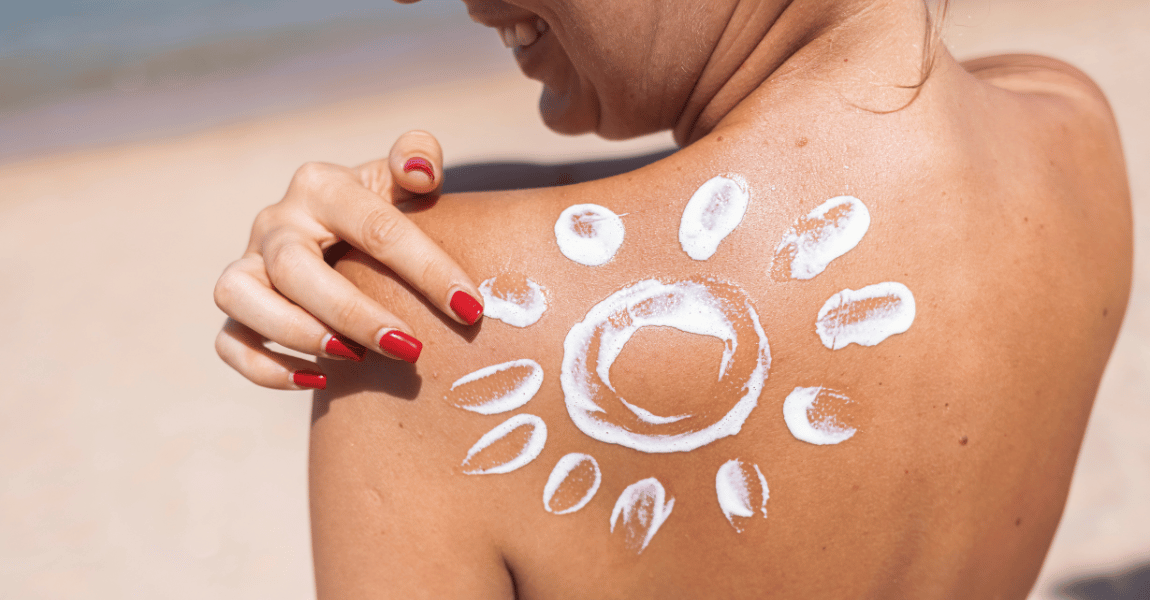
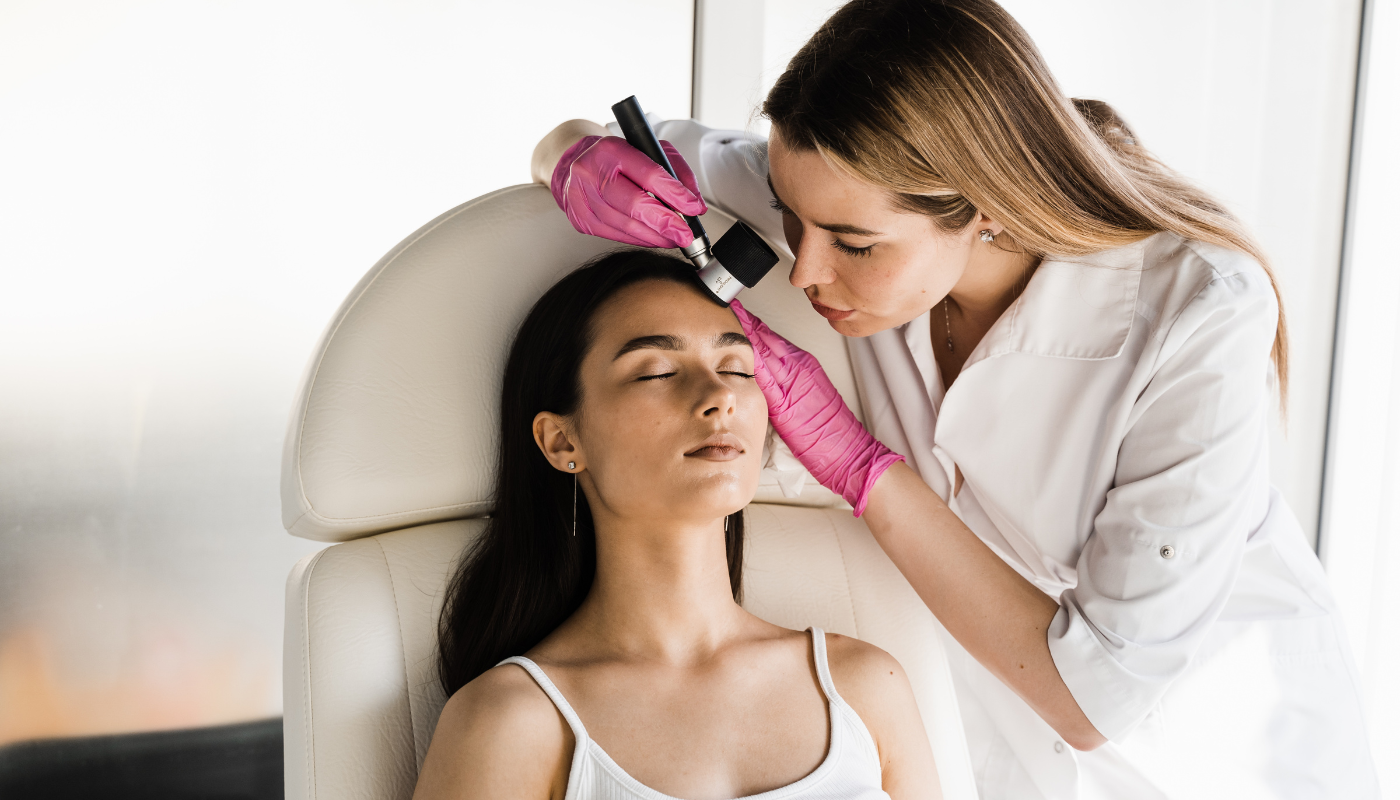
While anyone can develop skin cancer, certain factors increase the risk. Excessive sun exposure, fair skin, family history of the disease, older age, weakened immune system, and previous skin cancer diagnoses all contribute to an individual's susceptibility. Understanding these risk factors is essential for taking proactive measures to protect the skin and detect potential skin cancer early, increasing the chances of successful treatment. Remember to regularly examine your skin, wear protective clothing, apply sunscreen, and consult a healthcare professional for any concerning skin changes or symptoms.
More Skin Tips.
CoreBodi







| Powered by Kaptol Media


